Get Free Sample
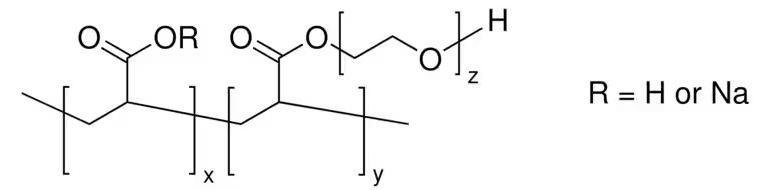
An in-depth study of the molecular structure of sodium polyacrylate【1】.
polymer sodium polyacrylate holds significant importance in modern materials due to its exceptional hydrophilic properties and versatile applications. The hydrophilic nature of sodium polyacrylate, stemming from its molecular structure with polar functional groups, allows it to attract and retain large amounts of water. This unique property makes it a valuable component in various applications.
In modern materials, sodium polyacrylate sap is widely used for its water-absorbing capabilities. Its versatility is evident in applications ranging from personal care products, like diapers, where it efficiently absorbs and retains moisture, to industrial settings, such as wastewater treatment, where it aids in effective water removal. Additionally, sodium polyacrylate plays a crucial role in agriculture by improving water efficiency in soil through the use of soil conditioners and water-absorbing polymers.

The adaptability of natrium polyacrylate across different industries highlights its significance as a key material contributing to advancements in water management, hygiene, and sustainable agricultural practices.
Sodium polyacrylate, a highly efficient superabsorbent polymer, finds diverse applications across multiple sectors.
sodium polyacrylic finds extensive use in various industrial applications owing to its remarkable water-absorption capabilities. One major application is in wastewater treatment processes, where it aids in efficient water removal, facilitating the separation of water from contaminants. Additionally, it is employed in industries dealing with moisture-sensitive materials, such as textiles. The hydrophilic nature of sodium polyacrylates makes it a valuable component in moisture control systems, ensuring the integrity and quality of materials susceptible to moisture damage. Its role in industrial hygiene products, such as superabsorbent materials in diapers, underscores its significance in maintaining product efficacy and user comfort.
Agricultural application
In agriculture, water gel sodium polyacrylate plays a vital role in enhancing water management practices. Incorporated into soil conditioners and water-absorbing polymers, it assists in retaining moisture in the soil. This proves especially beneficial in arid regions or during drought conditions, where water scarcity is a challenge. The ability of sodium polyacrylate biodegradable to absorb and release water gradually helps improve soil structure, reduce the frequency of irrigation, and enhance overall water efficiency in agricultural practices. Its application contributes to sustainable farming by optimizing water resources and promoting healthier plant growth.
sodium polyacrylate polymerization has spurred significant innovations in water-related technologies, showcasing its versatility and commitment to sustainability. One notable aspect is its biodegradability, aligning with the growing emphasis on eco-friendly solutions. Here are specific innovations:
Water Conservation Structures:
Sodium polyacrylate's biodegradable nature has been harnessed in the development of water conservation structures. These structures, made from sodium polyacrylate-based materials, are designed to absorb and retain rainwater or irrigation, gradually releasing it to the surrounding soil. This innovation promotes efficient water utilization in agriculture and landscaping while ensuring minimal environmental impact.
Biodegradable Water Retention Products:
In response to environmental concerns, there has been a shift towards developing biodegradable water retention products for various applications. Sodium polyacrylate, being biodegradable, is a key component in these products. They are utilized in landscaping, horticulture, and erosion control, offering effective water management solutions that break down naturally over time, minimizing ecological footprint.
Green Infrastructures for Urban Water Management:
Sodium polyacrylate's biodegradability has been instrumental in the creation of green infrastructures for urban water management. These include permeable pavements and green roofs designed with sodium polyacrylate-based materials that absorb and release rainwater, reducing runoff and contributing to sustainable urban water systems. This innovation addresses both water conservation and environmental impact concerns.
Biodegradable Water-Blocking Materials:
In construction and civil engineering, sodium polyacrylate in water is used in the development of biodegradable water-blocking materials. These materials, when exposed to water, form a gel-like barrier that prevents water infiltration in certain applications. The biodegradable nature ensures that, over time, the barrier breaks down naturally, reducing the need for long-term maintenance and minimizing environmental impact.
Sodium polyacrylate, often utilized in products requiring high water absorption, is generally regarded as non-biodegradable in natural environments due to its robust chemical structure.
As it degrades, polymer sodium polyacrylate undergoes a process where its complex molecular structure is gradually broken down into simpler, more bioavailable compounds. This biodegradation process can occur in various environments, including soil and water, where microorganisms consume the polymer as a source of carbon and nutrients.
Real examples of successful applications in different fields.
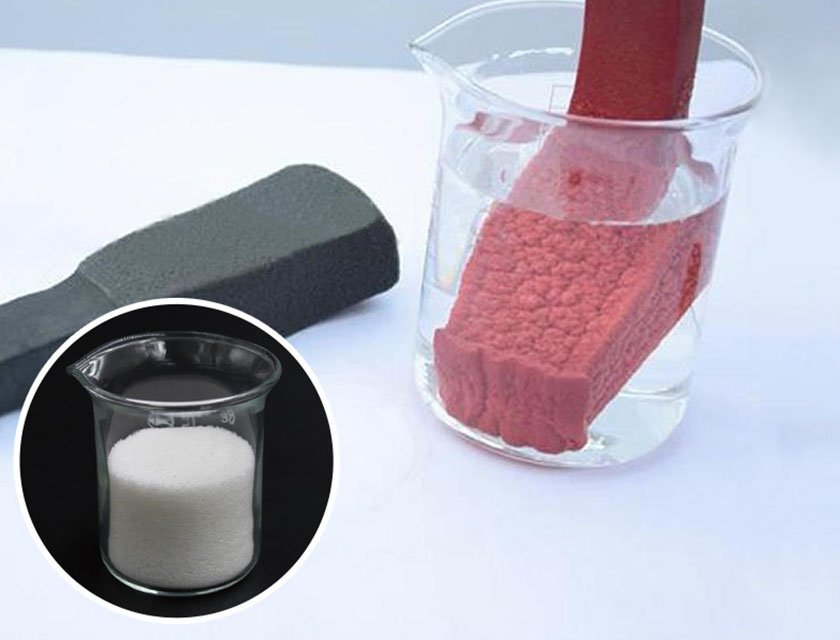

Background:
Expanded rubber, a versatile material known for its cushioning and insulation properties, has seen enhanced performance through the incorporation of sodium polyacrylate. This case study illustrates the practical application of sodium polyacrylate in expanding the capabilities of rubber materials.
To improve water absorption and retention in expanded rubber, making it suitable for applications where controlled water absorption is crucial.
Since super absorbent polymer is one of the main raw materials of expanding rubber, SOCO® Polymer is becoming the better choice in it because of its better water absorbent and water retention capacities. Besides SOCO® Polymer is harmless & eco-friendly, much safer to be used.
The incorporation of sodium polyacrylate into expanded rubber yielded several positive outcomes:
Improved Water Absorption:
The presence of sodium polyacrylate significantly increased the material's water absorption capacity, allowing it to absorb and retain water efficiently.
Controlled Water Release:
The hydrophilic nature of sodium polyacrylate facilitated controlled water release, ensuring that the expanded rubber maintained its structural integrity while providing controlled moisture absorption and release.
Enhanced Sealing Performance:
In gaskets and seals, the sodium polyacrylate-infused expanded rubber demonstrated improved sealing performance in environments with fluctuating moisture levels, making it suitable for diverse applications.
Application:
In the manufacturing of gaskets and seals, particularly those used in environments where exposure to water or moisture is a concern.
Background:
Drilling fluids, essential in the oil and gas industry, play a critical role in facilitating drilling operations. The incorporation of sodium polyacrylate in drilling fluid is a noteworthy case study demonstrating the advantages of this polymer in enhancing fluid performance during drilling processes.
To improve the stability and efficiency of drilling fluid, particularly in challenging geological conditions where wellbore instability and fluid loss are common issues.
SOCO® Polymer can be Drilling Fluid/Drilling Mud Additive, which is suitable for plumb shaft, horizontal well, deep shaft, etc.

Application:
Utilization of polymer sodium polyacrylate in the formulation of drilling fluid for oil and gas exploration and extraction.
The inclusion of sodium polyacrylate in the drilling fluid demonstrated several positive outcomes:
Enhanced Fluid Viscosity:
sap sodium polyacrylate contributed to improved fluid viscosity, aiding in the stability of the drilling fluid and reducing the risk of wellbore instability.
Effective Fluid Loss Control:
The polymer's water-absorbing capabilities proved effective in controlling fluid loss, ensuring that the drilling fluid maintained its integrity and functionality, even in porous formations.
Improved Drilling Efficiency:
Field trials revealed increased drilling efficiency, as the drilling fluid with sodium polyacrylate exhibited better performance in maintaining wellbore stability and preventing issues associated with fluid loss.
This case study highlights the successful application of sodium polyacrylate in drilling fluid, addressing challenges related to wellbore stability and fluid loss. The enhanced properties of the drilling fluid contribute to improved efficiency and reliability during oil and gas drilling operations, showcasing the valuable role of sodium polyacrylate in the industry.
Polyacrylate polymers are versatile materials with a wide range of applications across multiple industries.
Sodium Polyacrylate plays a vital role in modern materials science. Its unique properties of water absorption, water retention and thickening make it a key ingredient in many materials for high-tech and everyday applications.
Sodium polyacrylate, as a synthetic polymer, exhibits some biodegradability under certain conditions, although the rate and extent of complete degradation may be influenced by a variety of factors, such as environmental conditions, microbial species and abundance. sodium polyacrylate biodegradable is a water-soluble polymer electrolyte material that has been widely used in several fields.
Sodium polyacrylate is generally considered non-biodegradable under natural conditions.Versatile moisture adsorbing polymers are a class of materials designed to absorb and retain large amounts of moisture from their surroundings.
We have “Ask The Expert” online service 24/7. If you have any questions please contact us.